In JavaScript, the ternary operator offers a concise and powerful alternative to traditional conditional statements like if-else. This operator not only simplifies the code but also enhances readability when used appropriately. This detailed post will explore the syntax of the ternary operator, compare it with if conditions, demonstrate its use within template literals, and discuss the various aspects and advantages of using this operator.
Understanding the Syntax of the Ternary Operator
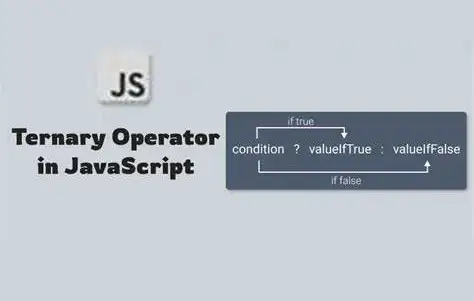
The ternary operator is essentially a compact form of the if-else statement that consists of three parts:
Syntax:
condition ? expressionIfTrue : expressionIfFalse;
In this syntax:
condition: Any expression that evaluates totrueorfalse.expressionIfTrue: The expression that is executed if the condition istrue.expressionIfFalse: The expression that is executed if the condition isfalse.
Comparison with the if Condition
Consider the following example using traditional if-else syntax:
let accessGranted;
if (userAge >= 18) {
accessGranted = 'Access granted';
} else {
accessGranted = 'Access denied';
}
Now, rewriting it with the ternary operator:
let accessGranted = userAge >= 18 ? 'Access granted' : 'Access denied';
In this example, the ternary operator reduces multiple lines of code into a single line, thereby simplifying the conditional logic without sacrificing readability.
Using the Ternary Operator within Template Literals
The ternary operator can be effectively used within template literals to incorporate conditional logic directly inside a string. Here’s an example:
const greeting = Hello, ${userAge >= 18 ? 'Adult' : 'Youngster'};
In this case, the ternary operator decides whether to label the user as an “Adult” or “Youngster” based on their age, directly embedding this logic within the template literal.
Different Aspects of the Ternary Operator
1) Nesting: Ternary operators can be nested to handle more complex conditions. However, excessive nesting can reduce clarity:
let result = score > 90 ? 'Excellent' : score > 75 ? 'Good' : 'Average';
2) Expression Evaluation: Always remember that the ternary operator evaluates to an expression, meaning it always returns a value.
3) Readability: While the ternary operator can compactify code, it should be used judiciously to maintain code readability. Avoid using it for overly complex conditions.
When to Use the Ternary Operator?
- Simple Conditionals: It is perfect for simple conditional assignments or when choosing between two values.
- Inline Operations: Useful in scenarios where conditional logic needs to be embedded within larger expressions or template literals.
Advantages of Using the Ternary Operator
- Conciseness: Reduces the boilerplate code required for
if-elsestatements. - Inline Expression Capability: Enables the inclusion of conditional logic within expressions without breaking flow.
- Clarity and Readability: Enhances readability when used appropriately by making the code less cluttered.
Conclusion
The ternary operator in JavaScript is a robust tool for developers looking to write concise and readable code. It provides a clear and succinct way to handle conditional logic, especially in scenarios requiring simple choices between two outcomes. By mastering the ternary operator, developers can streamline their code and efficiently integrate conditional expressions, thus making their JavaScript codebases more elegant and maintainable.